How to help someone who’s choking
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Watch
- 28 Jul 2022
- First Aid & CPR
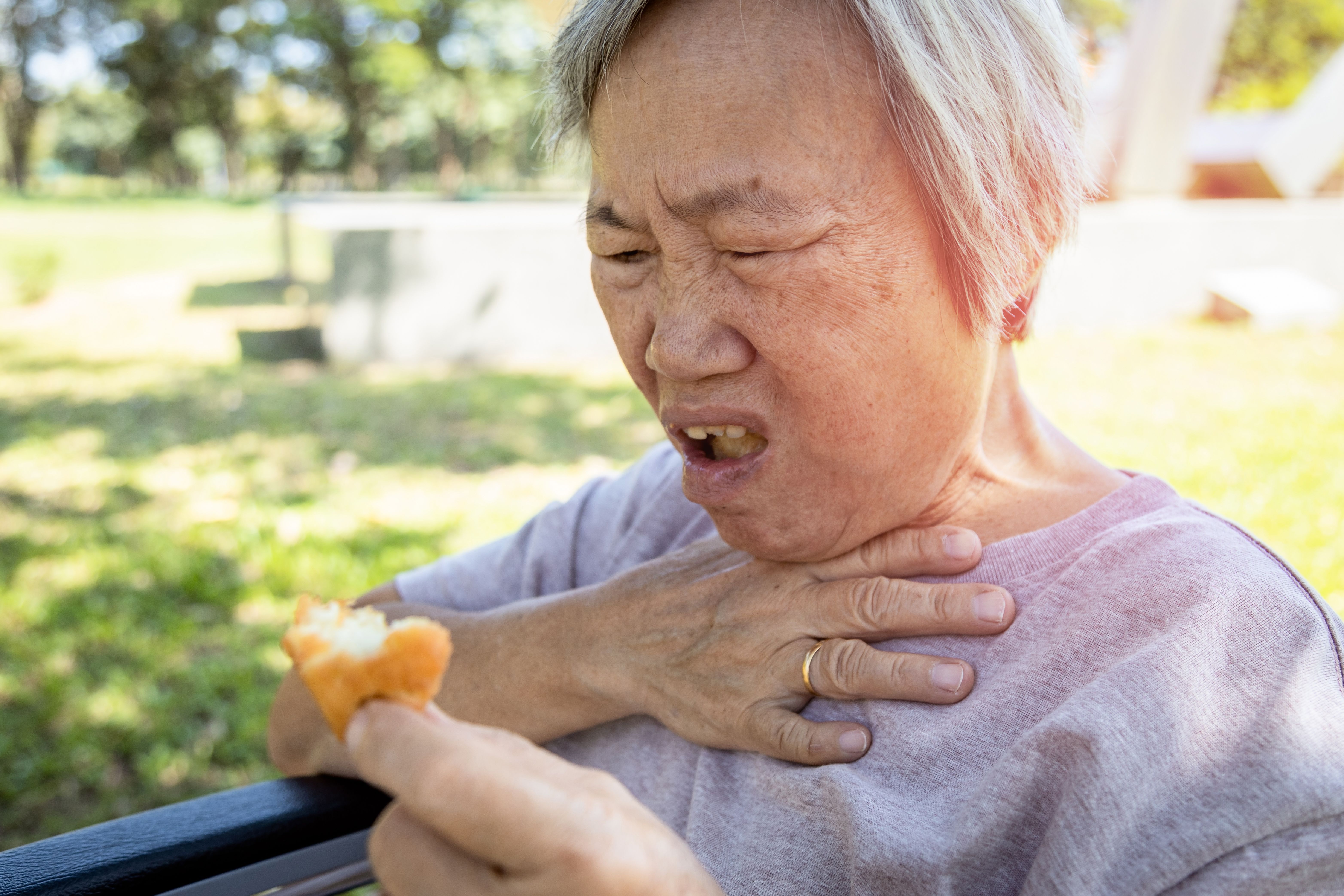

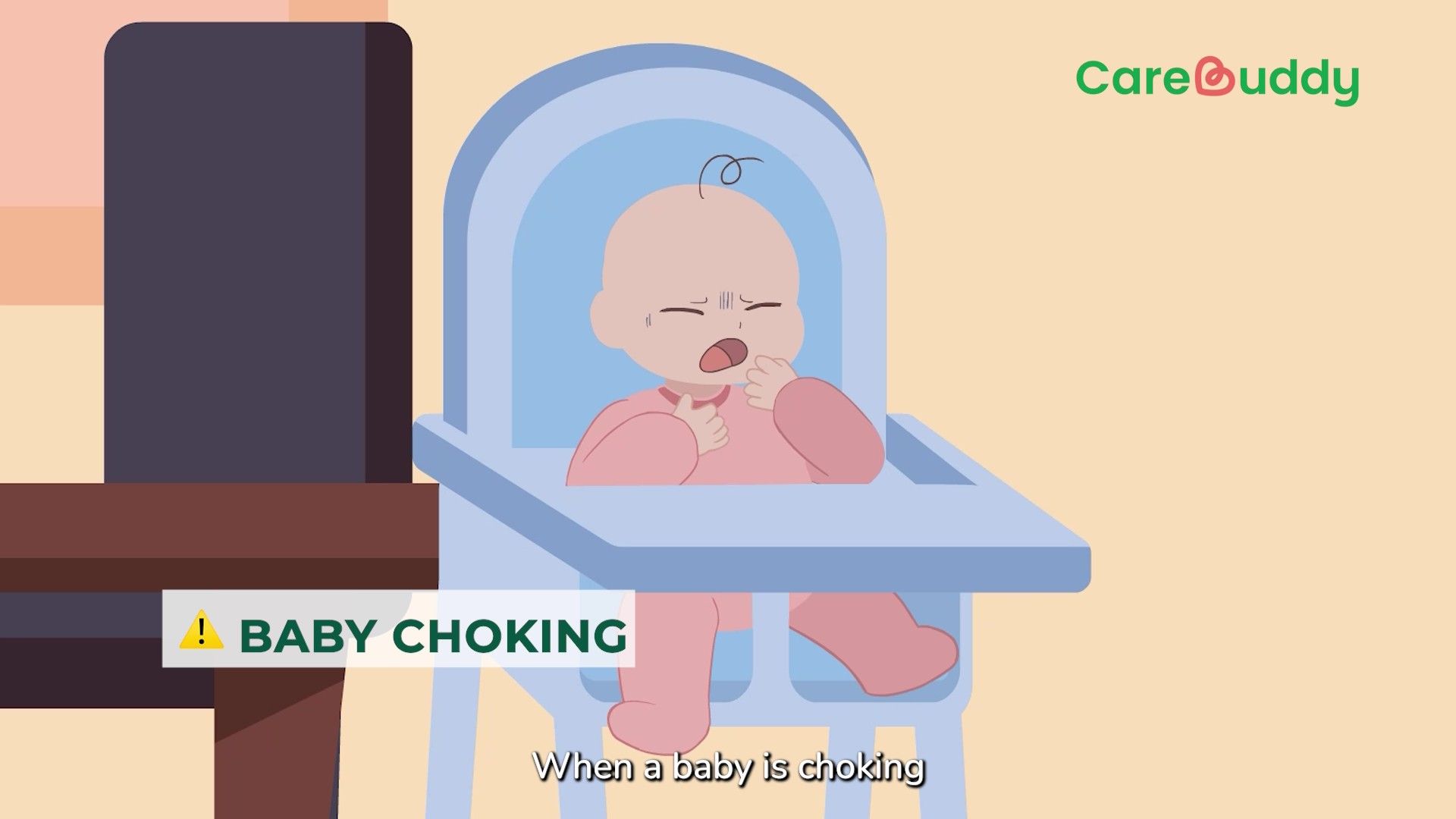
When a foreign body such as a piece of food blocks a person’s airway and impedes the breathing process, this is called foreign body airway obstruction (FBAO) or more simply, choking.
Because it impedes breathing which is the most essential process needed for living, choking is an immediate threat to life. This calls for swift and decisive action by anyone who happens to be around the sufferer when choking occurs.
What causes choking
There are two openings in the back of the mouth. The esophagus leads to the stomach. The trachea leads to the lungs. When swallowing occurs, a flap called the epiglottis covers the trachea. This ensures that the food enters the esophagus and goes to the stomach, instead of entering the trachea and going to the lungs.
When food is not chewed properly or the eater is talking or laughing while eating, the food is sometimes swallowed before the epiglottis covers the trachea, causing food to end up in the trachea where it gets stuck and causes choking.
Symptoms of choking
If an adult is choking, you may observe
- Coughing or gagging
- Hand signals and panic
- Sudden inability to talk
- Clutching the throat
- Wheezing
- Passing out
- Turning blue (seen earliest around face, lips and fingernail beds)
First aid for partial choking
Partial choking is when the person is coughing forcefully but is still able to speak. To ensure that partial choking does not lead to complete choking, encourage the person to cough out the impeding object until the obstruction is cleared.
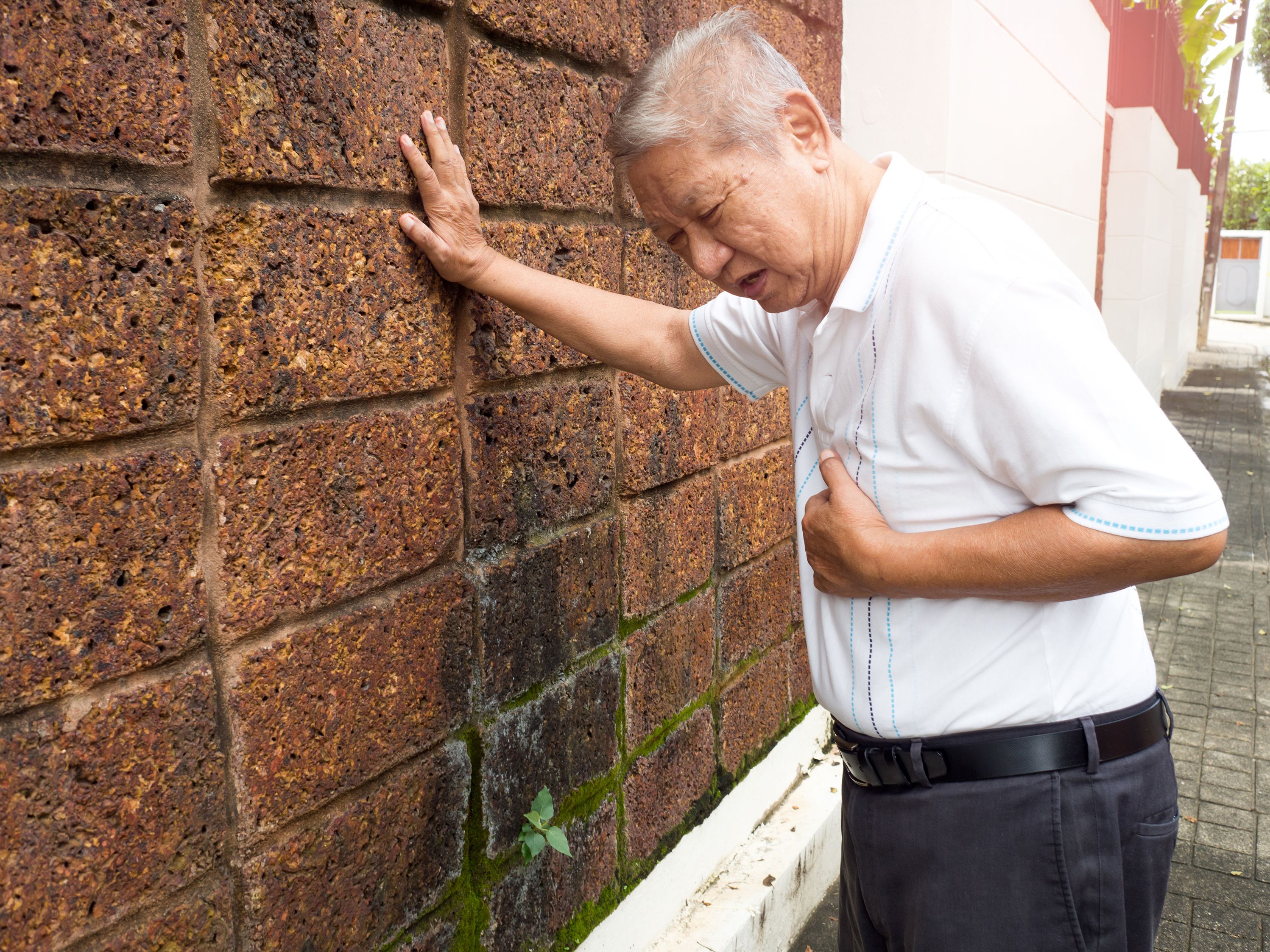
First aid for complete choking (person is conscious)
When the person cannot Speak, Breathe or Cough (SBC), it’s complete choking and they are in respiratory arrest. Call 995 for emergency medical assistance.
While you await professional medical help, provide immediate first aid in the form of abdominal thrusts (also known as Heimlich Maneuver) or chest thrusts (if the person is pregnant, obese or an infant).
Abdominal thrusts:
- Stand behind the person
- Clench a fist and place it right above their belly button
- Put your other hand on top of your fist and pull sharply inwards and upwards
- Repeat this movement until the object is expelled or the person becomes unconscious
Chest thrusts:
Similar to abdominal thrusts except that the hand position is higher up so as to be above the stomach or abdomen region.
First aid for complete choking (person is unconscious)
- Call 995 for emergency medical assistance. While you await that, follow the CAB sequence.
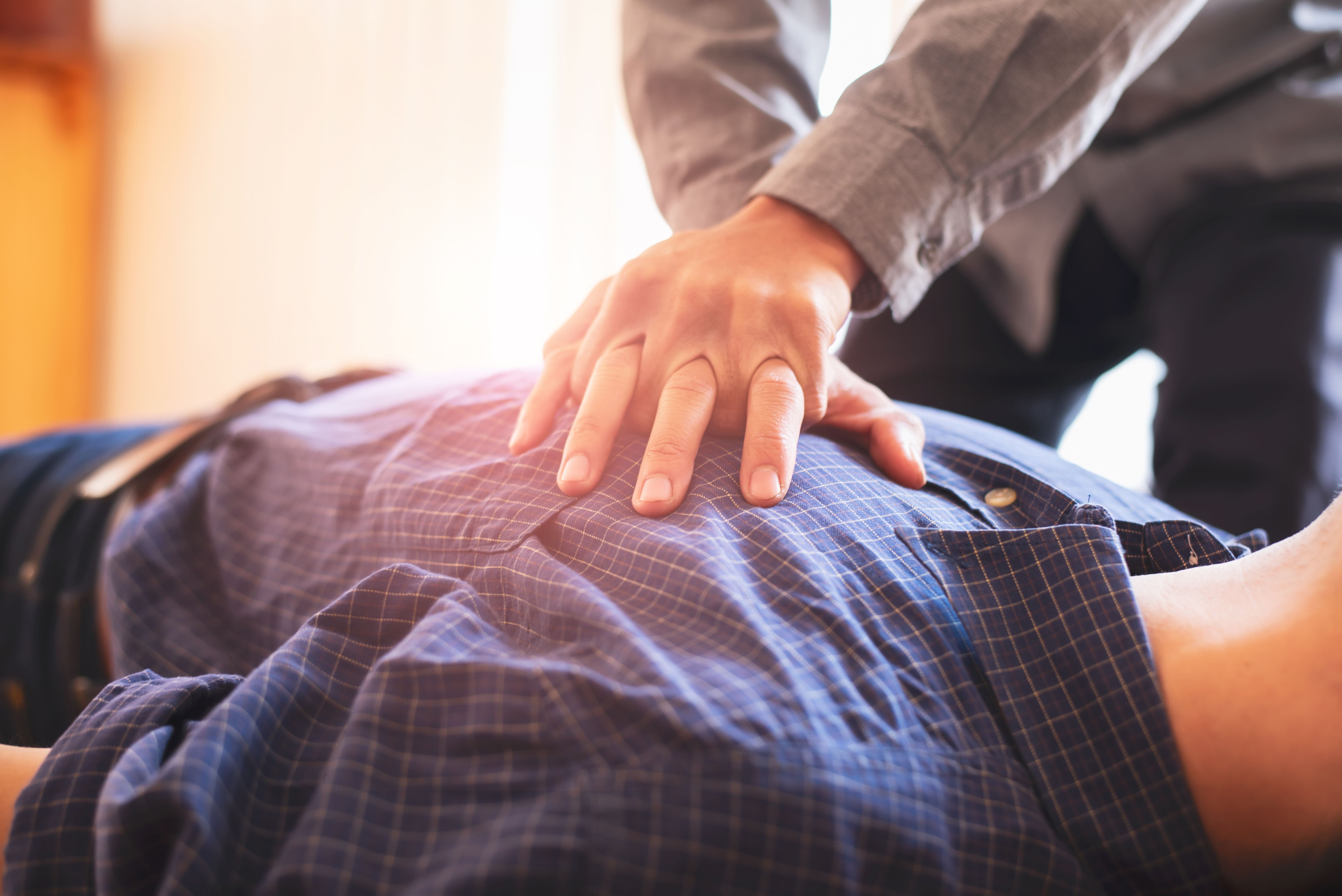
- Chest Compressions :Place the heels of your hands on the lower half of the sternum where the ribs come together. Interlock your fingers and perform a set of 30 chest compressions.
- Airway: Check the mouth to see if the impeding object has been displaced from the airway to the mouth. If it’s seen, remove it immediately.
- Breathing: Check breathing by looking at the rise and fall of the chest. If there’s no breathing, repeat the CAB sequence.
It’s important for more of us to learn how to respond to someone choking, because a choke can happen to anyone at any time. Having a bystander who knows what do to is a literal life-saver, so let’s aim to create as many of such bystanders as possible!
Article reviewed by David Tay, Senior Principal Educator (Nursing and Prehospital Care), HMI Institute