Preventing, managing and treating diabetes
- CareBuddy
- 4 Mins Watch
- 20 Sep 2022
- Common Health Issues

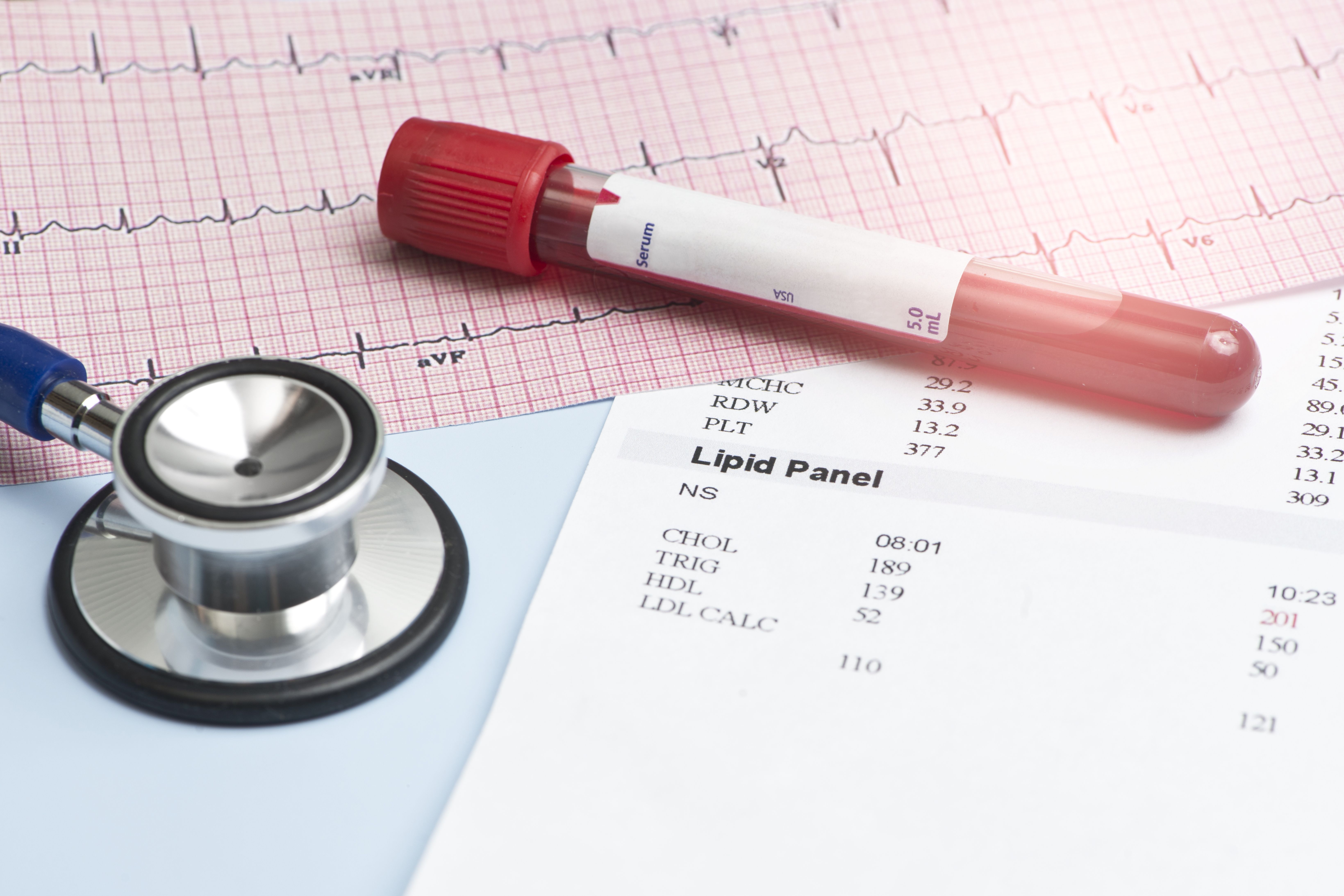
Diabetes is a chronic condition that results from the inability of the human body to correctly process glucose, a type of sugar. This is sometimes caused by insufficient production of insulin, the hormone that allows us to absorb glucose from the blood into our cells. Sometimes, even if sufficient insulin is produced, the body can lose sensitivity to the insulin, leading to the same problem. Either way, this causes glucose to stay in the blood instead of reaching our cells. This is why the most common measurable manifestation of diabetes is high blood glucose.
Types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a condition in which the body does not make insulin. Insulin is typically made in the pancreas, but in the case of Type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks and destroys the cells of the pancreas where insulin is made. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day through injections.
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by the body either not producing enough insulin, or losing sensitivity to it. Type 2 diabetes can start affecting a person at any age, though it occurs more commonly in middle-aged and older people.
Gestational diabetes develops in some pregnant women and fades away after the baby is born. However, gestational diabetes increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later.
Complications arising from diabetes
Over time, the consistently high blood glucose levels caused by diabetes can lead to
- Eye problems like diabetic retinopathy where the blood vessels in the eye are damaged by the high blood glucose
- Foot problems such as pain, tingling and loss of feeling, when peripheral nerves are damaged
- Heart disease and heart attacks
- Strokes
- Kidney problems
Preventing diabetes
With current medical knowledge, Type 1 diabetes can be difficult to prevent, but Type 2 diabetes can. Here’s how:
- Keep your weight within a healthy range (BMI < 23.5)
- Get at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity physical activity on at least 5 days a week
- Eat healthier foods like fruits and vegetables and reduce fatty foods and sugary drinks
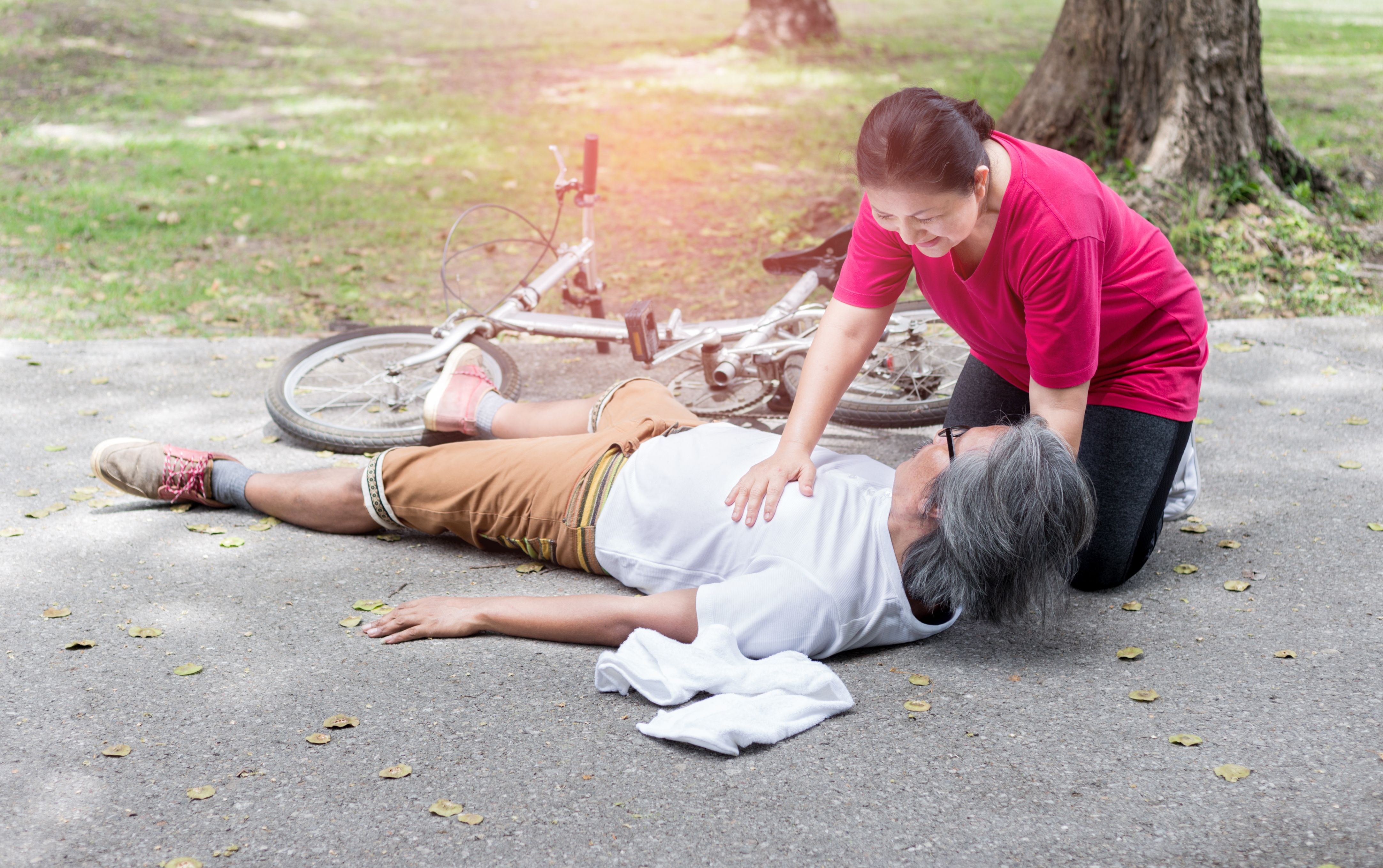
First aid for diabetic emergencies
The two types of diabetic emergencies are hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycemia (high blood glucose).
Hypoglycemia can be identified through symptoms such as
- Weakness, dizziness, confusion, hunger, tremors
- Sudden unconsciousness during or after physical exertion
- Behavioural changes such as anger
- Cold sweats
Hyperglycemia can be identified through symptoms such as
- Weakness and fatigue
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Intense thirst, dry skin, mouth and lips
- Irritability or confusion
- Drowsiness leading to unconsciousness
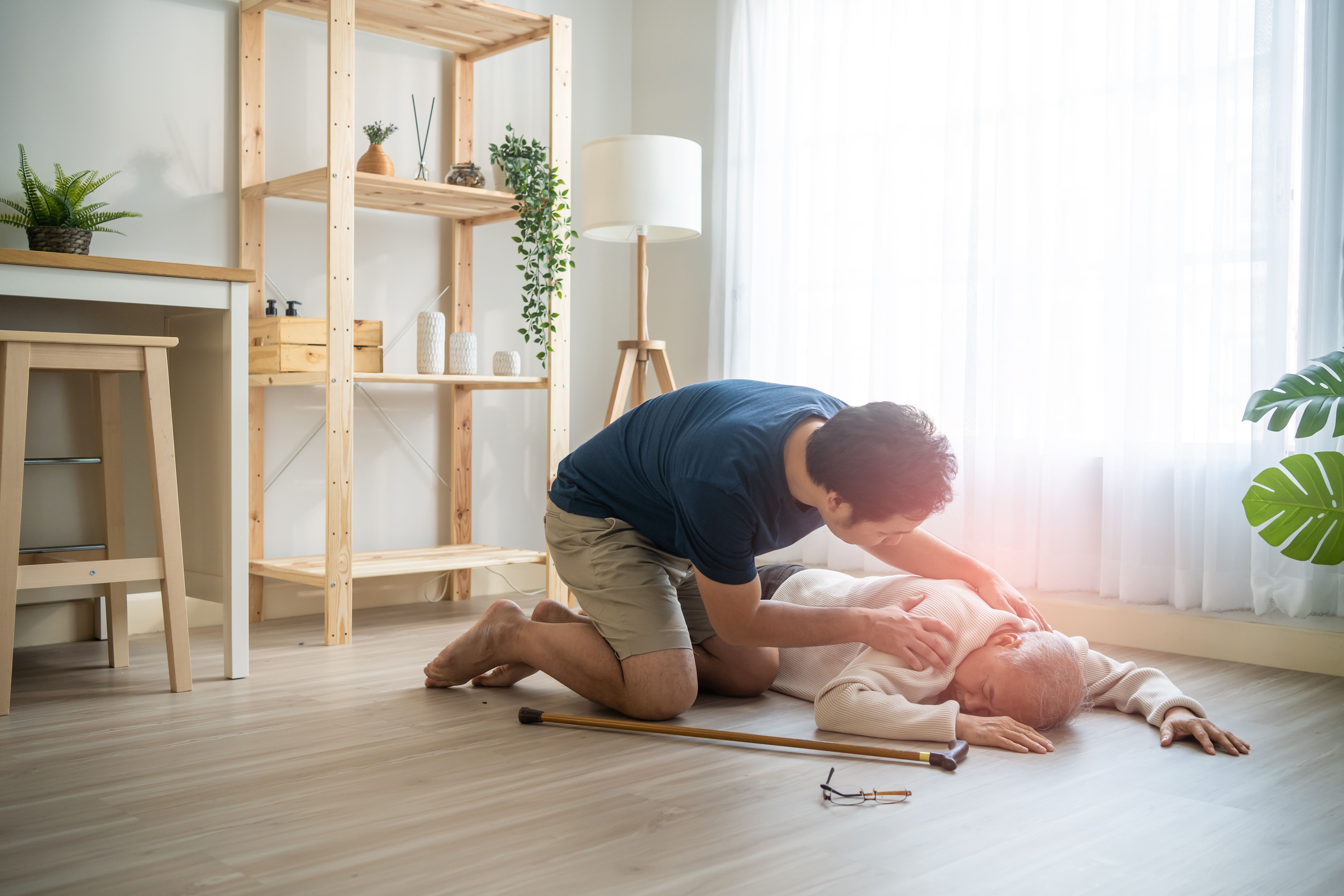
For both kinds of diabetic emergencies, first aid involves
- Checking ABC (Airway-Breathing-Circulation) and ensuring they continue to breath and their heart continues to pump if the person is unconscious.
- Checking the blood glucose levels if a hypocount machine is available
- Calling 995 for emergency medical help.
Treating diabetes long-term
Type 1 diabetes can be treated by
- Insulin injections
- Regular follow up with the doctor to ensure that tests are done on a regular basis to ensure good diabetic control and diabetes-related complications are picked up early
Type 2 diabetes can be treated by
- Lifestyle changes such as a healthier diet and more exercise
- Medication
- Insulin injections
- Regular follow up with the doctor to ensure that tests are done on a regular basis to ensure good diabetic control and diabetes-related complications are picked up early
As more parts of the world including Singapore experience a rapidly aging population, diabetes is one of the most common chronic conditions that will need to be managed. Through a combination of prevention, first aid and long-term treatment, we can help more of our people manage it better and continue to enjoy a high quality of life.
Article reviewed by Dr Kenneth Koh Eu Min, Medical Director and Co-founder, OneCare Medical.